|
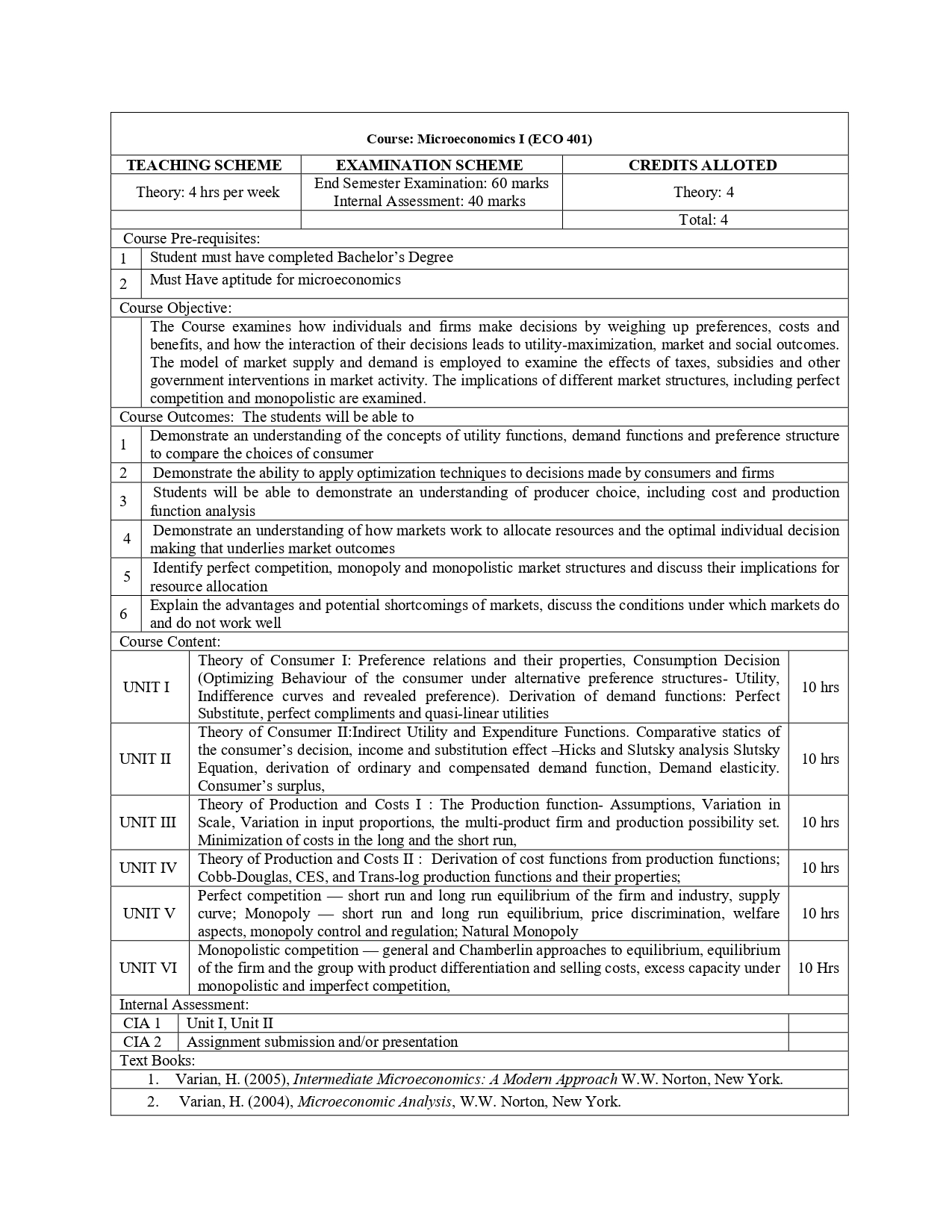
Course Objective: |
||
|
|
The Course examines how individuals and firms make decisions by weighing up preferences, costs and benefits, and how the interaction of their decisions leads to utility-maximization, market and social outcomes. The model of market supply and demand is employed to examine the effects of taxes, subsidies and other government interventions in market activity. The implications of different market structures, including perfect competition and monopolistic are examined. |
|
|
Course Outcomes: The students will be able to |
||
|
1 |
Demonstrate an understanding of the concepts of utility functions, demand functions and preference structure to compare the choices of consumer |
|
|
2 |
Demonstrate the ability to apply optimization techniques to decisions made by consumers and firms |
|
|
3 |
Students will be able to demonstrate an understanding of producer choice, including cost and production function analysis |
|
|
4 |
Demonstrate an understanding of how markets work to allocate resources and the optimal individual decision making that underlies market outcomes |
|
|
5 |
Identify perfect competition, monopoly and monopolistic market structures and discuss their implications for resource allocation |
|
|
6 |
Explain the advantages and potential shortcomings of markets, discuss the conditions under which markets do and do not work well |
|
|
Course Content: |
||
|
UNIT I Theory of Consumer I: Preference relations and their properties, Consumption Decision (Optimizing Behaviour of the consumer under alternative preference structures- Utility, Indifference curves and revealed preference). Derivation of demand functions: Perfect Substitute, perfect compliments and quasi-linear utilities |
10 hrs |
|
|
UNIT II Theory of Consumer II:Indirect Utility and Expenditure Functions. Comparative statics of the consumer’s decision, income and substitution effect –Hicks and Slutsky analysis Slutsky Equation, derivation of ordinary and compensated demand function, Demand elasticity. Consumer’s surplus, |
10 hrs |
|
|
UNIT III Theory of Production and Costs I : The Production function- Assumptions, Variation in Scale, Variation in input proportions, the multi-product firm and production possibility set. Minimization of costs in the long and the short run, |
10 hrs |
|
|
UNIT IV Theory of Production and Costs II : Derivation of cost functions from production functions; Cobb-Douglas, CES, and Trans-log production functions and their properties; |
10 hrs |
|
|
UNIT V Perfect competition — short run and long run equilibrium of the firm and industry, supply curve; Monopoly — short run and long run equilibrium, price discrimination, welfare aspects, monopoly control and regulation; Natural Monopoly |
10 hrs |
|
|
UNIT VI Monopolistic competition — general and Chamberlin approaches to equilibrium, equilibrium of the firm and the group with product differentiation and selling costs, excess capacity under monopolistic and imperfect competition, |
10 Hrs |
|
|
Text Books: |
||
|
1. Varian, H. (2005), Intermediate Microeconomics: A Modern Approach W.W. Norton, New York. |
||
|
||
|
Reference Books: |
||
|
1. Gravelle, H and Ray Rees (2004), Microeconomics, 3rd edition, Prentice Hall Longman London. |
||
|
2. Sen, A. (1999), Microeconomics : Theory and Applications, Oxford University Press, New |
||
|
3. Microeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions (Upper Level Economics Titles)Cengage; 11 edition (2014) |
||
|
||
|
5. Nicholson, W., Microeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions, eighth edition, South Western Thomson Learning, 2002 |
||
- Teacher: Department of Economics